Agentic AI: The Future of AI Workflows
Agentic AI: The Future of AI Workflows
A short summary of online course by Andrew Ng - DeepLearning.AI
As AI moves beyond single prompts and responses, Agentic AI is emerging as a new way to build systems that can plan, act, and iterate.
This post is a concise summary of an online course by Andrew Ng (DeepLearning.AI), with a focus on what Agentic AI really means for people building real products.
Non-Agentic vs Agentic AI
- Non-agentic workflow (zero-shot):
- Ask → Answer (straightforward)
- Ask ChatGPT to write an eassy for me…
- Agentic workflow:
- Thinking + Research → Revision → Back to thinking…
- Similar to Claude code where it understand user’s prompt, decide and list tasks or code, write a code, summarize what it’s done…
So, what is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to workflows where multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) act as agents collaborating to accomplish tasks by:
- Using specialized models for different purposes (text-to-image, voice-to-text, etc.)
- Leveraging tools like web search, database operations, and code execution
- Working together to tackle complex problems through coordinated effort
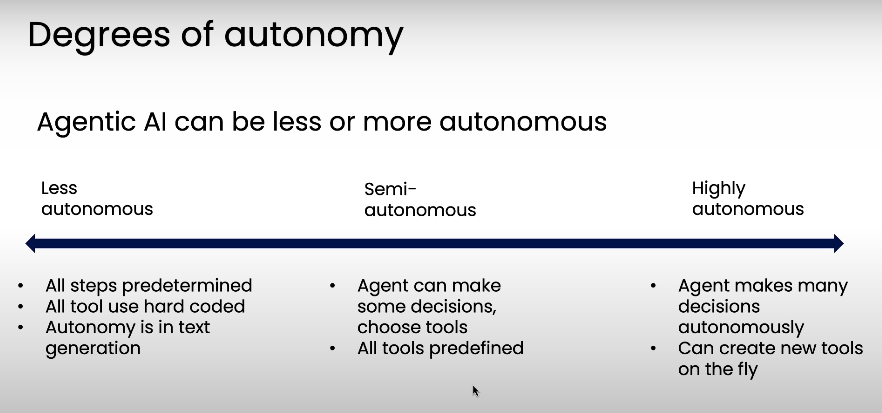
Rather than debating what constitutes a "true" agent, Andrew Ng introduces a spectrum of autonomy, where systems can be categorized as having less, semi, or high autonomy.
Core Design Patterns in Agentic AI
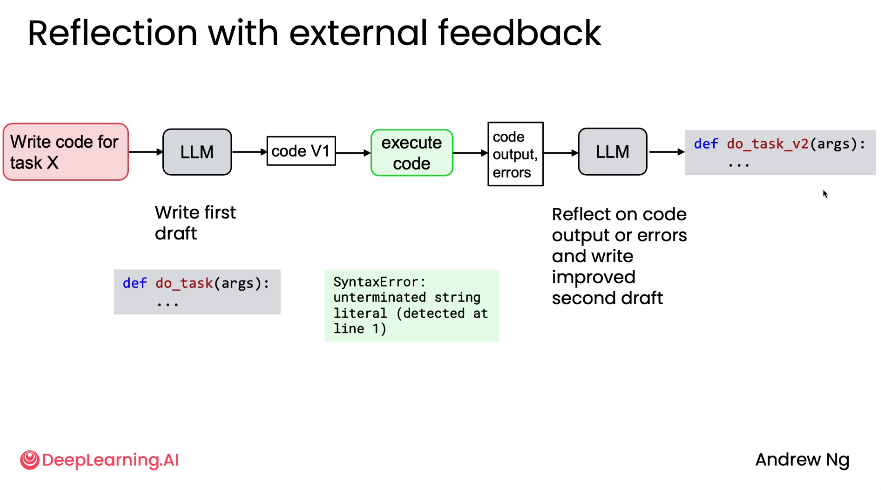
1. Reflection
This pattern uses multiple LLMs where one performs a task and another evaluates it:
- Example: One agent writes code while another reviews and identifies bugs
- The feedback loop creates significantly improved outputs compared to single-model approaches
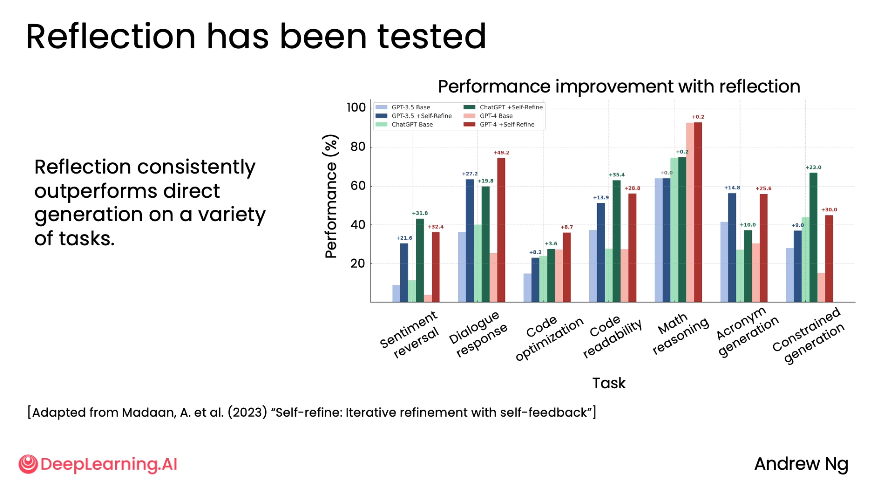
Instead of using zero-shot prompt (no example in prompt) → using reflection helped improve output significantly
2. Tool Use
Enabling LLMs to access external tools dramatically expands their capabilities:
- Web search for up-to-date information
- Code execution to perform complex calculations
- Database operations to store and retrieve information
- Example query: "What's the best hotel in Bangkok?" → LLM conducts web search
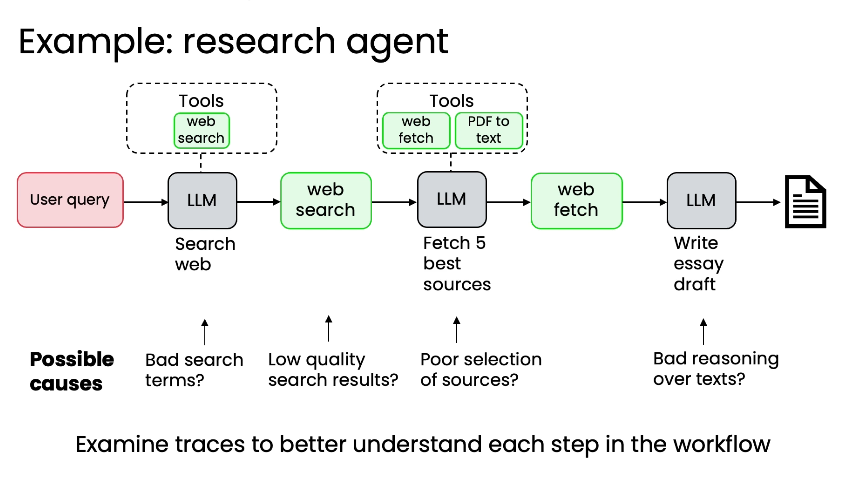
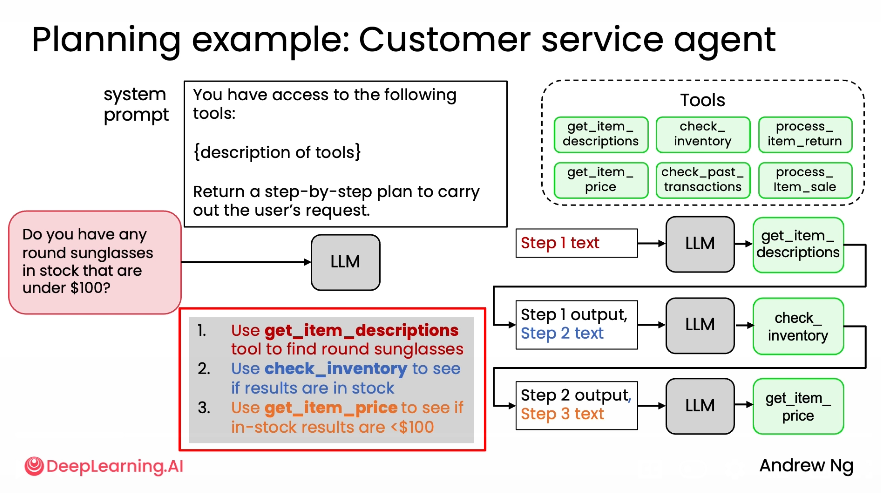
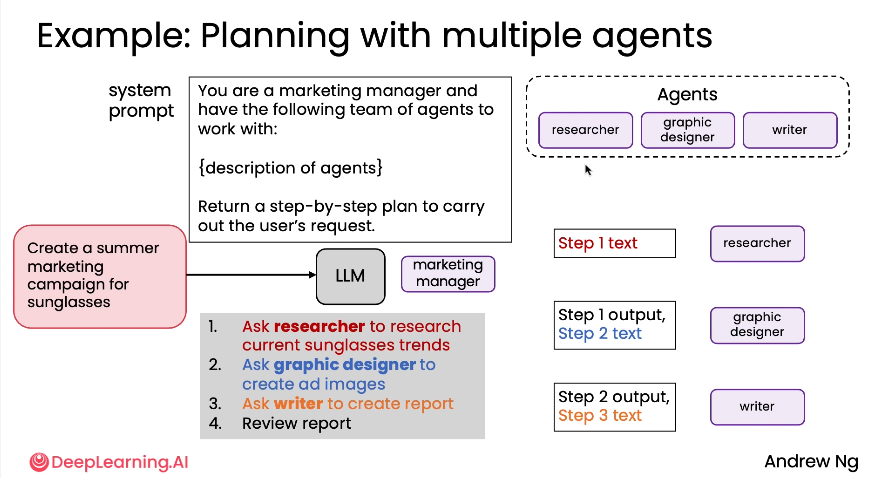
3. Planning
- Breaking down complex multi-step tasks
- Creating structured plans for execution
- Try to build quick & dirty and see if its working or not before develop it further
- As you find places where your evals fail to capture human judgement as to what system is better, use that as an opportunity to improve the metric
- Look for places where performance is worse than humans
- Example: invoice processing workflow → test quick and dirty system and found that we should put the most effort on eval the date since its mixed up dates output between due date and invoice date…
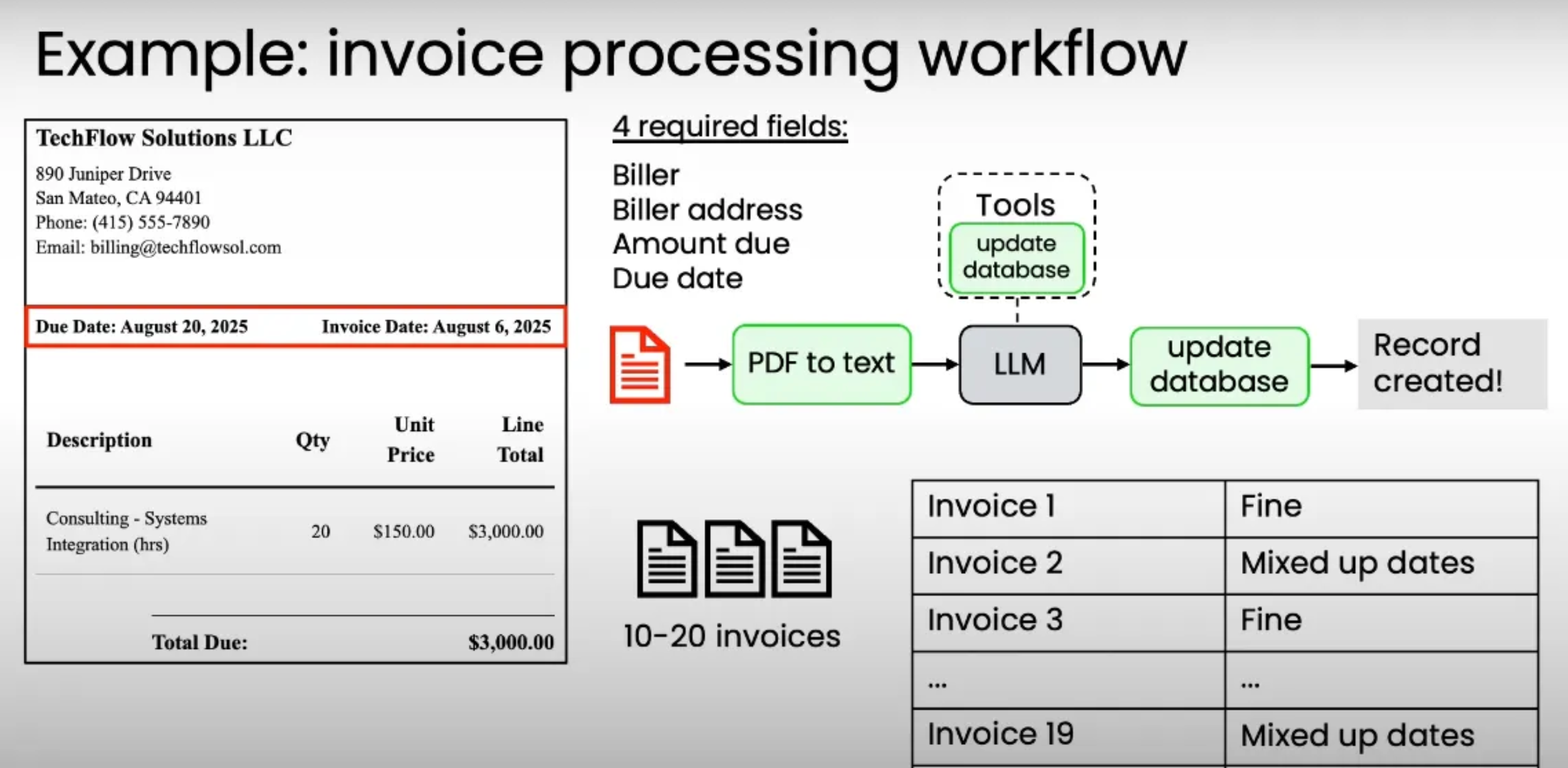
- Instead of relying on LLM to extract → create a tools e.g. date extraction function to let LLM extract accurately date data

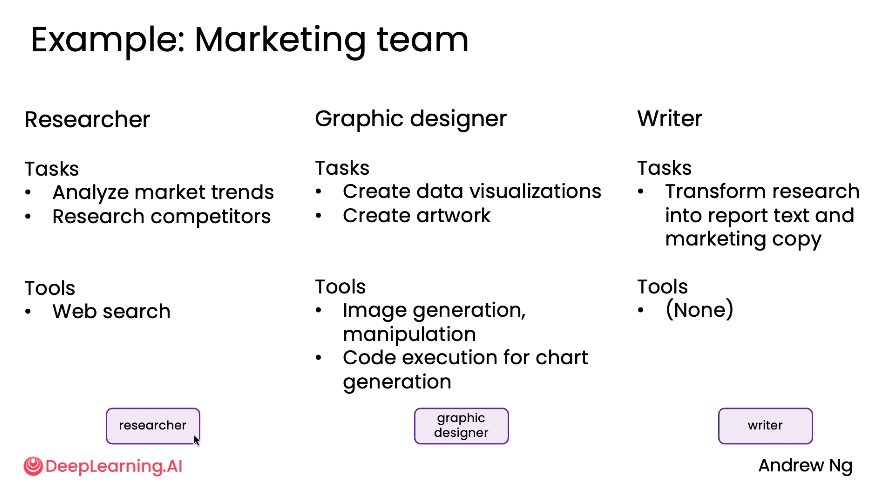
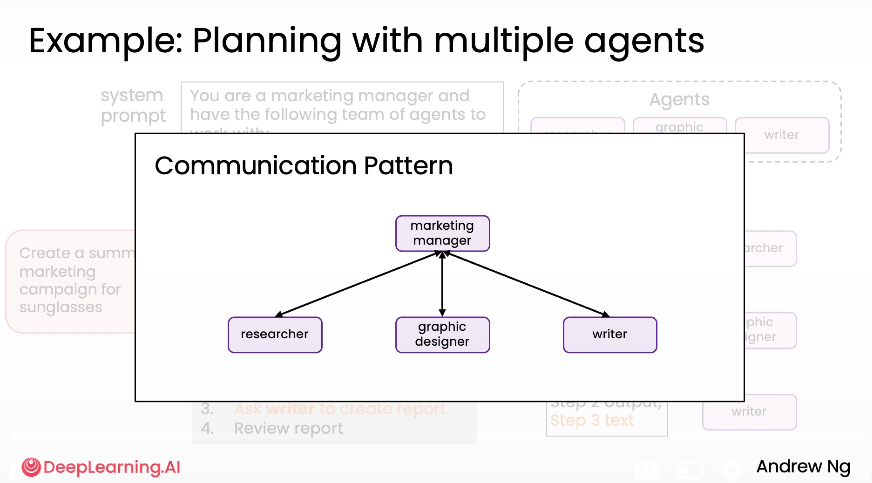
4. Multi-agent Collaboration
Multiple specialized agents working together like a team:
- Different roles (designer, developer, researcher, marketer, etc.)
- Various communication patterns (linear, hierarchical)
- Enhanced problem-solving through specialization
Similar to hiring a team of PM + Designer + Dev to build an app… Multi-Agentic workflows can be like that…
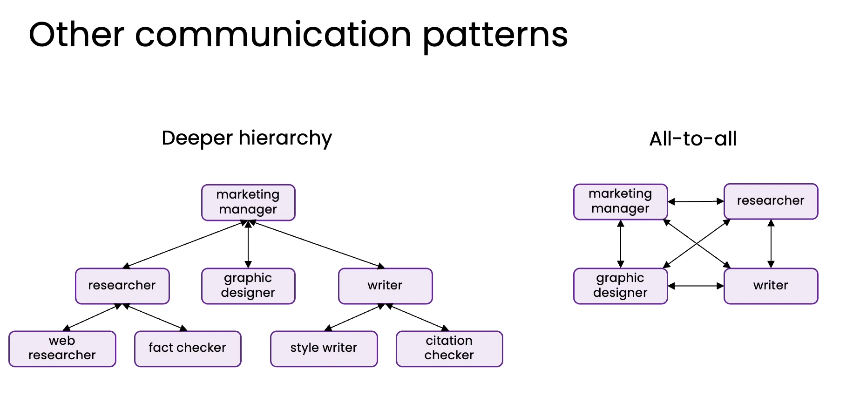
- There are many ways to design the communication pattern for multi-agent workflows
- Communication Patterns for multi-agents systems
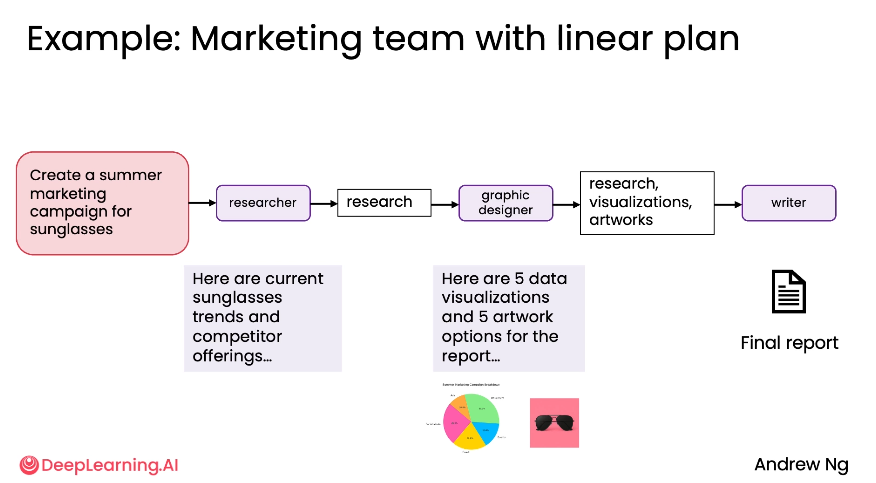
- Linear Communication patterns - Agents work in sequence, with each one passing its output to the next agent in line.
- Linear Communication patterns - Agents work in sequence, with each one passing its output to the next agent in line.
- Communication Patterns for multi-agents systems
- Hierarchy Communication patterns
- Other Communicatioan patterns
Benefits of Agentic AI
- Performance: Multiple specialized agents often outperform single models
- Increased Speed: Parallel processing allows faster completion than human teams
- Modularity: Easy to add or update tools, swap models, or modify workflows
- Adaptability: Can handle complex, multi-step problems through planning
Development Process for Agentic Systems
The recommended approach is:
- Build quick prototypes to test concepts ("quick & dirty")
- Identify performance gaps through testing
- Create specialized tools to address weaknesses
- Iteratively improve based on evaluation results
Practical Applications
Agentic AI can be applied to numerous domains:
- Invoice processing systems
- Customer service agents
- Data analysis workflows
- Content creation pipelines
- Research assistants
Conclusion
By breaking complex tasks into manageable components and leveraging specialized models and tools, these systems can achieve higher levels of performance and autonomy than traditional approaches.
The future of AI lies not just in making individual models more powerful, but in designing intelligent workflows where multiple models collaborate effectively - much like human teams do in the real world.
In the next post, I’ll share how I use these ideas to build my own Agentic AI workflow in my app.
